- February 18, 2020
- Posted by: EARSC
- Categories: EARSC News, European EO Industry
Authors: Barbara Riedler & Stefan Lang, Department of Geoinformatics – Z_GIS
Copernicus Academy – an emerging network
The Copernicus Academy network connects universities, research institutions, business schools, private and public organizations with the aim to facilitate cooperation in research, education and training and thus linking research & academia with authorities & service providers to boost the use of Copernicus data and information services. With currently more than 160 members – including from outside Europe – the Copernicus Academy has been growing into an invaluable pool of experts with application know-how, emerging from pooling the various types of expertise – trans-national, trans-domain and trans-sectoral.
Copernicus Knowledge and Innovation Hubs
To harvest on this invaluable expertise, the DT-SPACE-07-BIZ-2018 funded action CopHub.AC (www.cophub-ac.eu) fosters knowledge and innovation hubs, demonstrating several technical and procedural pillars to showcases and link ongoing R&D activities in Copernicus-relevant academic fields, as well as to sustain the innovation process from academia to businesses on the highest possible scientific and technical level.
Core activities focus around
(1) Invent – visualizing research outcome and the distributed expertise, both in thematic and methodological aspects
(2) Inform – reaching out to administrations and the public at large
(3) Innovate –bridging the gap between academia and industry through monitoring innovation and uptake
(4) Interact – bringing Copernicus Academy members together with stakeholders and users
The idea of such Copernicus Knowledge and Innovation hubs is to stimulate the uptake and evolution of information services derived from space and in-situ data through
• physical implementation in form of regional centers of excellence/science hubs focusing on interaction with local as well as regional stakeholders and outreach/information events ((2) and (4); Fig.1)

• virtual hubs – development of technical components to visualize and facilitate easy harvesting of information about the expertise of Copernicus Academy member, both within the network and for potential external cooperation partners ((1) and (3)). A focus is set on methodological skills, educational offers, the innovation level of the Copernicus Academy member and their thematic expertise, including the involvement in Copernicus services. For the latter special Thematic working groups with experts in the specific Copernicus services exchanging (methodological) ideas, finding future priority themes and potential targets groups have been initialized (Fig.2).

Visualizing capacities and innovation
This ambition to be realized requires an advanced and dynamic visualization on an easily accessible and amenable web interface that captures both the current geographic pattern of distributed capacities within the Copernicus Academy and its adoption of new technical trends, scientific achievements, and innovation.
Therefore, a new gateway to the Copernicus Academy is formed which goes beyond the mere capturing of contact and organizational details of its members and additionally includes information about educational offers and cooperation with other Copernicus Academy members. Furthermore self-assessment of the members in ranked expertise of the following aspects is inquired as a basis for visualization purpose as well as to gain more knowledge about members and understand their potential offer:
• Methodology – know-how in state-of-the-art technologies and methods applied in the research fields of the Copernicus Academy member ranging from AI to Geovisualisation
• Copernicus services – related expertise and involvement in the six Copernicus services Land, Marine, Climate Change, Atmosphere, Emergency and Security
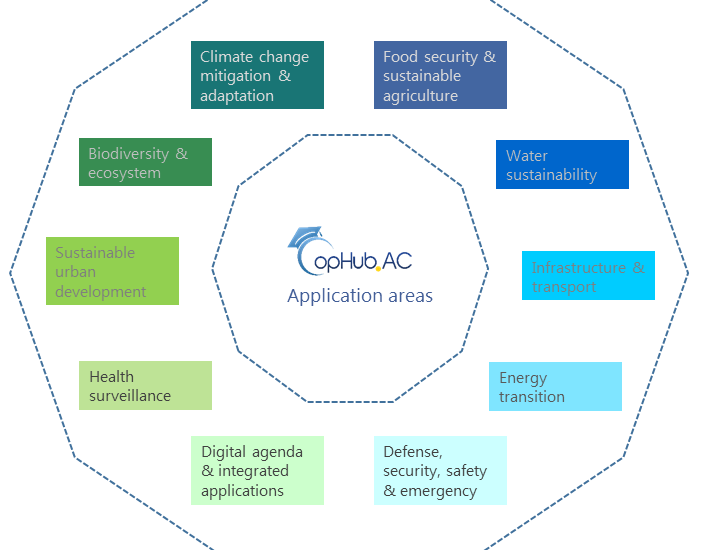
• Application areas – thematic expertise in ten selected fields including societal benefit areas & Horizon Europe areas as main blocks (Fig.3)

For the monitoring of innovation, an indicator-based approach is planned, that is updated in regular reports complemented by retrieved information harvested by semantic web technology. There will be five dimensions covered, each described by a set of proxies (Fig.4):
• Innovators – including knowledge transfer, reasearch-uptake and patents
• Linkages & Partnerships – cooperation with different stakeholders in form of projects, publications or awards
• Attractiveness of research system – internationality of the institution and scientific output
• Copernicus related activities – including participation in Copernicus events and networks, use of Copernicus data, development of related training material and involvement in Copernicus services
• Education – types of educational offers

